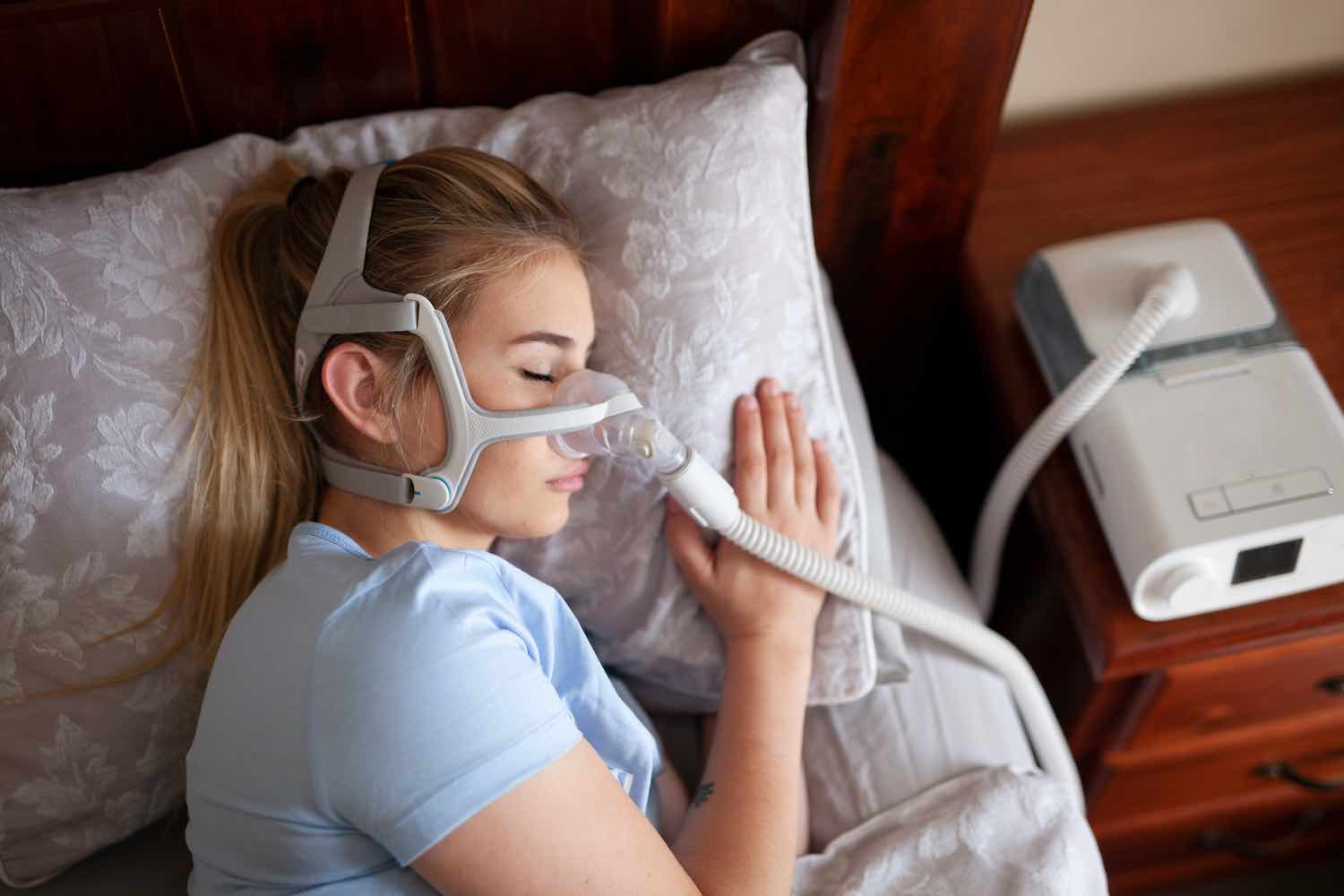
In today’s fast-paced world, it’s essential to prioritize our health and well-being. One vital aspect of our overall health is respiratory care. Breathing freely allows us to live life to the fullest and tackle any challenges that come our way.
However, many individuals face respiratory issues that hinder their ability to breathe comfortably. One solution that has revolutionized respiratory care is the cpap machine Australia.
What is a CPAP Machine?
A CPAP machine, short for Continuous Positive Airway Pressure machine, is a medical device primarily used to treat sleep apnea. Sleep apnea is a common sleep disorder characterized by pauses in breathing or shallow breaths during sleep. These pauses can last for a few seconds to minutes and can occur multiple times throughout the night. Sleep apnea can lead to daytime sleepiness, fatigue, and other health issues if left untreated.
A CPAP machine delivers a continuous flow of pressurized air through a mask worn over the nose or mouth, ensuring the airway remains open throughout the night. This pressurized air acts as a splint, preventing the collapse of the airway and allowing for normal breathing. By providing a constant and steady stream of air, the CPAP machine helps to eliminate or reduce the frequency of sleep apnea episodes, allowing individuals to experience a restful and uninterrupted night’s sleep.
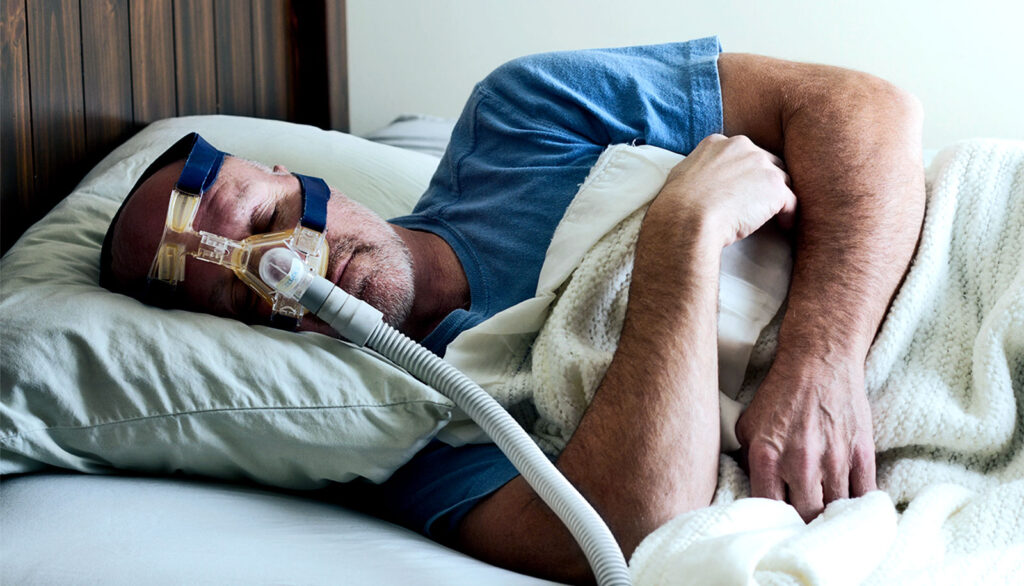

The Basic Components of a CPAP Machine
A typical CPAP machine consists of several key components. The main unit contains the air compressor, which generates the pressurized air, and a motor that controls its delivery. The air compressor works by drawing in room air and pressurizing it to the desired level before delivering it to the user through the mask.
Another important component is the mask, which comes in various styles to accommodate individual preferences. The mask is designed to fit securely over the nose, mouth, or both, creating a seal to ensure that the pressurized air is delivered directly into the airway. The mask should be comfortable to wear and properly fitted to prevent air leaks, which can reduce the effectiveness of the therapy.
Lastly, the CPAP machine is equipped with a humidifier to add moisture to the delivered air. The pressurized air from the machine can sometimes cause dryness and discomfort in the airway and nasal passages. The humidifier helps to alleviate these symptoms by adding moisture, making the therapy more comfortable and tolerable for the user.
How Does a CPAP Machine Work?
The CPAP machine’s operation is straightforward yet highly effective. When the machine is turned on, it pressurizes the air and delivers it through the mask into the airway. This constant flow of air acts as a splint, keeping the airway open and preventing obstructions that cause sleep apnea episodes.
By ensuring a consistent air supply, the CPAP machine promotes uninterrupted breathing throughout the night, leading to a better quality of sleep. The continuous positive airway pressure also helps to prevent the collapse of the upper airway, which is the main cause of sleep apnea. This allows individuals with sleep apnea to experience a significant reduction in the frequency and severity of apnea episodes, resulting in improved overall health and well-being.
It is important to note that the use of a CPAP machine requires a proper diagnosis of sleep apnea by a healthcare professional. The machine should be prescribed and set up by a qualified sleep specialist to ensure the correct pressure settings and mask fit for optimal treatment.
In addition to treating sleep apnea, CPAP machines are also used in other respiratory conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and congestive heart failure. These machines provide a similar function of delivering pressurized air to help maintain open airways and improve breathing.
Overall, CPAP machines have revolutionized the treatment of sleep apnea and other respiratory conditions. They have significantly improved the quality of life for individuals suffering from these disorders, allowing them to enjoy restful and rejuvenating sleep.
The Role of CPAP Machines in Respiratory Care
CPAP machines play a crucial role in managing a range of respiratory conditions, with the primary focus on sleep apnea. However, these devices are not limited to sleep apnea treatment alone. They can also be beneficial for individuals with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
When it comes to respiratory care, CPAP machines have become indispensable tools. These devices have revolutionized the way we treat sleep apnea, a common sleep disorder characterized by pauses in breathing or shallow breaths during sleep. These interruptions can significantly impact a person’s sleep quality and overall health. Fortunately, CPAP machines are highly effective in managing this condition.
Treating Sleep Apnea with CPAP
CPAP, which stands for Continuous Positive Airway Pressure, is a therapy that involves delivering a continuous flow of pressurized air to the airways through a mask worn over the nose or mouth. This constant flow of air acts as a splint, preventing the collapse of the airway and allowing individuals with sleep apnea to breathe comfortably while asleep.
By ensuring a steady supply of oxygen, CPAP machines help maintain adequate airflow throughout the night, reducing the frequency and severity of breathing interruptions. This, in turn, improves sleep quality and helps alleviate the symptoms associated with sleep apnea, such as excessive daytime sleepiness, fatigue, and morning headaches.
Moreover, CPAP therapy has been shown to have additional benefits beyond sleep apnea treatment. Research has indicated that using CPAP machines can help lower blood pressure, reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases, and improve overall cognitive function.

CPAP in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
While CPAP machines are widely known for their effectiveness in managing sleep apnea, their utility extends beyond that. Individuals with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), a progressive lung disease that obstructs airflow, can also benefit from CPAP therapy.
In COPD, the airways become narrowed, making it challenging to fully exhale and causing breathlessness. CPAP machines can be used as a complementary treatment option in COPD management. By providing a constant positive pressure during exhalation, these machines aid in airway clearance techniques, helping to remove excess mucus and improving lung function.
Furthermore, CPAP therapy can enhance breathing efficiency in individuals with COPD. By delivering a continuous flow of pressurized air, CPAP machines help maintain optimal oxygenation levels, reducing the strain on the respiratory muscles and making breathing easier.
It is important to note that CPAP therapy for COPD should be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional, as it may not be suitable for all individuals with the condition. A thorough evaluation of the patient’s respiratory status and individual needs is necessary to determine the appropriateness of CPAP as part of their treatment plan.
In conclusion, CPAP machines have revolutionized respiratory care, particularly in the management of sleep apnea. These devices provide a continuous flow of pressurized air, preventing airway collapse and allowing individuals to breathe comfortably while asleep. Moreover, CPAP therapy has shown potential benefits in COPD management, aiding in airway clearance techniques and improving breathing efficiency. As technology continues to advance, CPAP machines are likely to play an even more significant role in respiratory care, improving the quality of life for individuals with various respiratory conditions.
The Benefits of Using CPAP Machines
Using a CPAP machine offers numerous advantages to improve overall well-being, especially in individuals with respiratory conditions.
CPAP, which stands for Continuous Positive Airway Pressure, is a highly effective treatment for sleep apnea and other respiratory conditions. It involves wearing a mask that delivers a constant flow of air pressure, keeping the airways open and allowing for uninterrupted breathing throughout the night.
Improving Sleep Quality
One of the primary benefits of CPAP therapy is the significant improvement in sleep quality. By ensuring uninterrupted breathing throughout the night, CPAP machines help individuals achieve a deeper and more restful sleep. This leads to increased energy levels, improved cognition, and enhanced overall mood.
When individuals with sleep apnea use a CPAP machine, they no longer experience the frequent interruptions in breathing that characterize the condition. This means that they can enjoy a full night’s sleep without waking up gasping for air or feeling excessively tired in the morning.
Furthermore, CPAP therapy helps to reduce the occurrence of other sleep disorders, such as snoring and sleep fragmentation. Snoring is often a symptom of sleep apnea, and the use of CPAP machines can effectively eliminate this disruptive and potentially harmful habit.
Reducing Daytime Fatigue
Due to the improved sleep quality, individuals using CPAP machines experience reduced daytime fatigue. Sleep apnea can disrupt normal sleep patterns, resulting in excessive daytime sleepiness and reduced productivity. With the use of CPAP therapy, individuals can wake up feeling refreshed, energized, and ready to tackle their daily activities.
Imagine being able to go through the day without constantly feeling the need to take a nap or struggling to stay awake during important tasks. CPAP therapy can make this a reality by providing individuals with the restful sleep they need to function optimally during the day.
By reducing daytime fatigue, CPAP machines also contribute to improved mental health. Chronic sleep deprivation can lead to mood swings, irritability, and even depression. With the consistent use of CPAP therapy, individuals can experience a significant improvement in their overall mood and emotional well-being.
Lowering Blood Pressure
Untreated sleep apnea can contribute to high blood pressure, increasing the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular complications. CPAP therapy effectively reduces blood pressure levels by ensuring consistent airflow and reducing the stress on the cardiovascular system. By maintaining healthy blood pressure levels, CPAP machines contribute to long-term cardiovascular health.
When individuals with sleep apnea use a CPAP machine, the constant flow of air pressure helps to keep their airways open and prevents the occurrence of apnea episodes. This reduces the strain on the heart and blood vessels, leading to a decrease in blood pressure levels.
Studies have shown that individuals who consistently use CPAP therapy experience a significant reduction in their blood pressure readings. This not only lowers the risk of cardiovascular complications but also improves overall heart health and reduces the need for medication to control hypertension.
In addition to lowering blood pressure, CPAP therapy has been found to improve other cardiovascular markers, such as reducing the risk of arrhythmias and improving endothelial function. These benefits further contribute to the long-term cardiovascular health of individuals using CPAP machines.
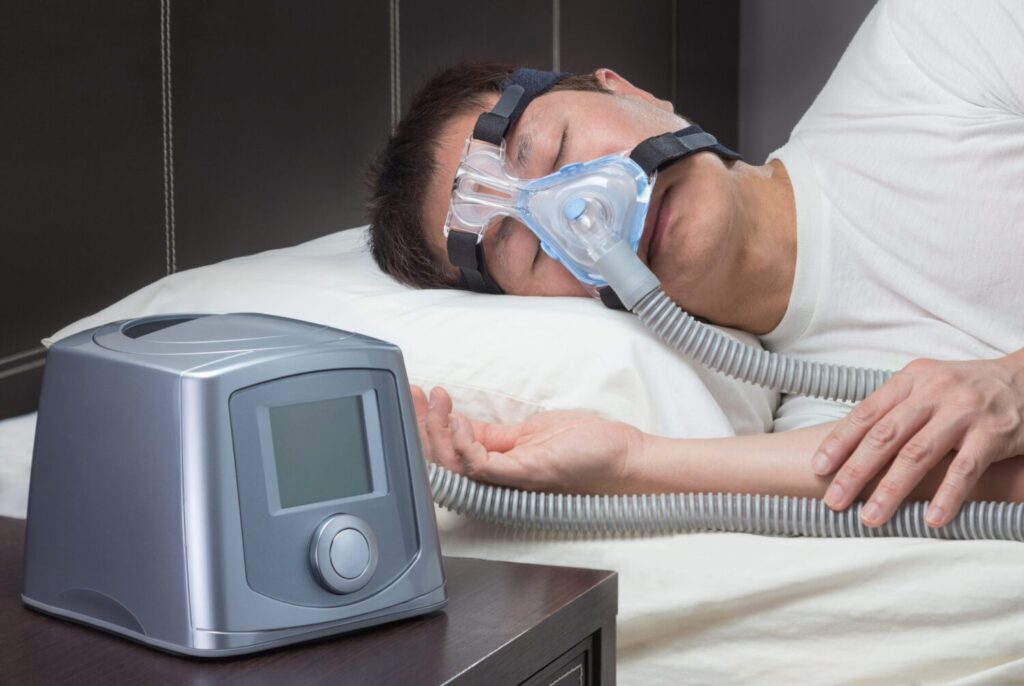
Overcoming Challenges of Using CPAP Machines
While CPAP machines offer significant benefits, some individuals face challenges when starting their therapy. It’s essential to address these obstacles to ensure successful long-term use.
Dealing with Discomfort
Some individuals may experience discomfort when first using a CPAP machine. This discomfort can include dryness in the nose or mouth, mask-related issues, or nasal congestion. However, these challenges can be overcome by working closely with healthcare professionals to find the most suitable mask style, adjusting humidity settings, or incorporating nasal sprays or airway moisturizers.
Addressing Noise Concerns
CPAP machines do produce a gentle humming sound while in operation. However, modern CPAP models are designed to minimize noise levels. Additionally, white noise machines or earplugs can be used to further reduce any noise-related concerns, ensuring an uninterrupted and peaceful night’s sleep.
The Future of CPAP Machines in Respiratory Care
As technology continues to advance, so do CPAP machines and their potential applications in respiratory care.
Technological Advancements in CPAP Machines
Ongoing research and development efforts have led to exciting technological advancements in CPAP machines. These innovations include improved mask designs for enhanced comfort, quieter motors, and advanced algorithms that tailor the therapy to individual needs. These technological advancements aim to make CPAP therapy more user-friendly and effective.
The Increasing Accessibility of CPAP Therapy
With the growing recognition of respiratory conditions and their impact on overall health, the accessibility of CPAP therapy is expanding. More healthcare providers and insurance companies are recognizing the importance of CPAP machines and the benefits they provide. This increased accessibility ensures that individuals with respiratory conditions can access and afford the respiratory care they need.
Conclusion
CPAP machines have transformed respiratory care, particularly in the treatment of sleep apnea. They offer a simple yet powerful solution to ensure uninterrupted breathing and improved sleep quality. Beyond sleep apnea, CPAP machines also play a role in managing COPD and offer numerous benefits, including enhanced sleep quality, reduced fatigue, and better cardiovascular health. While challenges may arise, they can be overcome with the support of healthcare professionals. The future of CPAP machines holds exciting possibilities with technological advancements and increased accessibility, ensuring a brighter future for respiratory care.
More to read: Minimally Invasive Glaucoma Surgery (MIGS)